Description
An array is a group of similar typed variables that are referred to by a common name. Arrays of any type can be created and may have one or more dimensions. A specific element in an array is accessed by its index. Array is simple type of data structure which can store primitive variable or objects. For example, imagine if you had to store the result of six subjects we can do it using array. To create an array value in Java, you use the new keyword, just as you do to create an object.
Defining and constructing one dimensional array
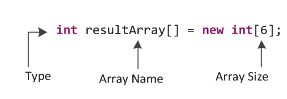
Here, type specifies the type of variables (int, boolean, char, float etc) being stored, size specifies the number of elements in the array, and array-name is the variable name that is reference to the array. Array size must be specified while creating an array. If you are creating a int[], for example, you must specify how many int values you want it to hold (in above statement resultArray[] is having size 6 int values). Once an array is created, it can never grow or shrink.
Initializing array: You can initialize specific element in the array by specifying its index within square brackets. All array indexes start at zero.
resultArray[0]=69;
This will initialize first element (index zero) of resultArray[] with integer value 69. Array elements can be initialized/accessed in any order. In memory it will create structure similar to below figure.
Array Literals
The null literal used to represent the absence of an object can also be used to represent the absence of an array. For example:
String [] name = null;
In addition to the null literal, Java also defines special syntax that allows you to specify array values literally in your programs. This syntax can be used only when declaring a variable of array type. It combines the creation of the array object with the initialization of the array elements:
String[] daysOfWeek = {“Sunday”, “Monday”, “Tuesday”, “Wednesday”, “Thursday”, “Friday”, “Saturday”};
This creates an array that contains the seven string element representing days of the week within the curly braces. Note that we don't use the new keyword or specify the type of the array in this array literal syntax. The type is implicit in the variable declaration of which the initializer is a part. Also, the array length is not specified explicitly with this syntax; it is determined implicitly by counting the number of elements listed between the curly braces.
Let’s see sample java program to understand this concept better. This program will help to understand initializing and accessing specific array elements.
package arrayDemo;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class ResultListDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Array Declaration
int resultArray[] = new int[6];
//Array Initialization
resultArray[0]=69;
resultArray[1]=75;
resultArray[2]=43;
resultArray[3]=55;
resultArray[4]=35;
resultArray[5]=87;
//Array elements access
System.out.println("Marks of First Subject- "+ resultArray[0]);
System.out.println("Marks of Second Subject- "+ resultArray[1]);
System.out.println("Marks of Third Subject- "+ resultArray[2]);
System.out.println("Marks of Fourth Subject- "+ resultArray[3]);
System.out.println("Marks of Fifth Subject- "+ resultArray[4]);
System.out.println("Marks of Sixth Subject- "+ resultArray[5]);
}
}
Alternative syntax for declaring, initializing of array in same statement
int [] resultArray = {69,75,43,55,35,87};
Multidimensional Arrays
In Java, multidimensional arrays are actually arrays of arrays. These, as you might expect, look and act like regular multidimensional arrays. However, as you will see, there are a couple of subtle differences. To declare a multidimensional array variable, specify each additional index using another set of square brackets. For example, the following declares a two dimensional array variable called twoDim. This will create matrix of the size 2x3 in memory.
int twoDim[][] = new int[2][3];
Let’s have look at below program to understand 2-dimentional array
package arrayDemo;
public class twoDimArrayDemo {
public static void main (String []args){
int twoDim [][] = new int [2][3];
twoDim[0][0]=1;
twoDim[0][1]=2;
twoDim[0][2]=3;
twoDim[1][0]=4;
twoDim[1][1]=5;
twoDim[1][2]=6;
System.out.println(twoDim[0][0] + " " + twoDim[0][1] + " " + twoDim[0][2]);
System.out.println(twoDim[1][0] + " " + twoDim[1][1] + " " + twoDim[1][2]);
}
}
Output
Inbuilt Helper Class (java.util.Arrays) for Arrays Manipulation:
Java provides very important helper class (java.util.Arrays) for array manipulation. This class has many utility methods like array sorting, printing values of all array elements, searching of element, copy one array into other array etc. Let’s see sample program to understand this class for better programming. In below program float array has been declared. We are printing the array elements before sorting and after sorting.
package arrayDemo;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class ArraySortingDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Declaring array of float elements
float [] resultArray = {69.4f,75.3f,43.22f,55.21f,35.87f,87.02f};
System.out.println("Array Before Sorting- " + Arrays.toString(resultArray));
//below line will sort the array in ascending order
Arrays.sort(resultArray);
System.out.println("Array After Sorting- " + Arrays.toString(resultArray));
}
}
Output
Similar to “java.util.Arrays” System class also has functionality of efficiently copying data from one array to another. Syntax as below,
public static void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos,Object dest, int destPos, int length)
The two Object arguments specify the array to copy from and the array to copy to. The three int arguments specify the starting position in the source array, the starting position in the destination array, and the number of array elements to copy.
Important points:
You will get “ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException” if you try access an array with an illegal index, that is with a negative number or with a number greater than or equal to its size.
Arrays are widely used with loops (for loops, while loops). There will be more sample program of arrays with loops tutorial.
Summary
An array is a group of similar typed variables that are referred to by a common name.
Array can be declared using indexes or literals.
Single dimensional array is widely used but we can have multi-dimensional.
An array is a group of similar typed variables that are referred to by a common name. Arrays of any type can be created and may have one or more dimensions. A specific element in an array is accessed by its index. Array is simple type of data structure which can store primitive variable or objects. For example, imagine if you had to store the result of six subjects we can do it using array. To create an array value in Java, you use the new keyword, just as you do to create an object.
Defining and constructing one dimensional array
Here, type specifies the type of variables (int, boolean, char, float etc) being stored, size specifies the number of elements in the array, and array-name is the variable name that is reference to the array. Array size must be specified while creating an array. If you are creating a int[], for example, you must specify how many int values you want it to hold (in above statement resultArray[] is having size 6 int values). Once an array is created, it can never grow or shrink.
Initializing array: You can initialize specific element in the array by specifying its index within square brackets. All array indexes start at zero.
resultArray[0]=69;
This will initialize first element (index zero) of resultArray[] with integer value 69. Array elements can be initialized/accessed in any order. In memory it will create structure similar to below figure.
Array Literals
The null literal used to represent the absence of an object can also be used to represent the absence of an array. For example:
String [] name = null;
In addition to the null literal, Java also defines special syntax that allows you to specify array values literally in your programs. This syntax can be used only when declaring a variable of array type. It combines the creation of the array object with the initialization of the array elements:
String[] daysOfWeek = {“Sunday”, “Monday”, “Tuesday”, “Wednesday”, “Thursday”, “Friday”, “Saturday”};
This creates an array that contains the seven string element representing days of the week within the curly braces. Note that we don't use the new keyword or specify the type of the array in this array literal syntax. The type is implicit in the variable declaration of which the initializer is a part. Also, the array length is not specified explicitly with this syntax; it is determined implicitly by counting the number of elements listed between the curly braces.
Let’s see sample java program to understand this concept better. This program will help to understand initializing and accessing specific array elements.
package arrayDemo;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class ResultListDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Array Declaration
int resultArray[] = new int[6];
//Array Initialization
resultArray[0]=69;
resultArray[1]=75;
resultArray[2]=43;
resultArray[3]=55;
resultArray[4]=35;
resultArray[5]=87;
//Array elements access
System.out.println("Marks of First Subject- "+ resultArray[0]);
System.out.println("Marks of Second Subject- "+ resultArray[1]);
System.out.println("Marks of Third Subject- "+ resultArray[2]);
System.out.println("Marks of Fourth Subject- "+ resultArray[3]);
System.out.println("Marks of Fifth Subject- "+ resultArray[4]);
System.out.println("Marks of Sixth Subject- "+ resultArray[5]);
}
}
Output
Alternative syntax for declaring, initializing of array in same statement
int [] resultArray = {69,75,43,55,35,87};
Multidimensional Arrays
In Java, multidimensional arrays are actually arrays of arrays. These, as you might expect, look and act like regular multidimensional arrays. However, as you will see, there are a couple of subtle differences. To declare a multidimensional array variable, specify each additional index using another set of square brackets. For example, the following declares a two dimensional array variable called twoDim. This will create matrix of the size 2x3 in memory.
int twoDim[][] = new int[2][3];
Let’s have look at below program to understand 2-dimentional array
package arrayDemo;
public class twoDimArrayDemo {
public static void main (String []args){
int twoDim [][] = new int [2][3];
twoDim[0][0]=1;
twoDim[0][1]=2;
twoDim[0][2]=3;
twoDim[1][0]=4;
twoDim[1][1]=5;
twoDim[1][2]=6;
System.out.println(twoDim[0][0] + " " + twoDim[0][1] + " " + twoDim[0][2]);
System.out.println(twoDim[1][0] + " " + twoDim[1][1] + " " + twoDim[1][2]);
}
}
Output
Inbuilt Helper Class (java.util.Arrays) for Arrays Manipulation:
Java provides very important helper class (java.util.Arrays) for array manipulation. This class has many utility methods like array sorting, printing values of all array elements, searching of element, copy one array into other array etc. Let’s see sample program to understand this class for better programming. In below program float array has been declared. We are printing the array elements before sorting and after sorting.
package arrayDemo;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class ArraySortingDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Declaring array of float elements
float [] resultArray = {69.4f,75.3f,43.22f,55.21f,35.87f,87.02f};
System.out.println("Array Before Sorting- " + Arrays.toString(resultArray));
//below line will sort the array in ascending order
Arrays.sort(resultArray);
System.out.println("Array After Sorting- " + Arrays.toString(resultArray));
}
}
Output
Similar to “java.util.Arrays” System class also has functionality of efficiently copying data from one array to another. Syntax as below,
public static void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos,Object dest, int destPos, int length)
The two Object arguments specify the array to copy from and the array to copy to. The three int arguments specify the starting position in the source array, the starting position in the destination array, and the number of array elements to copy.
Important points:
You will get “ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException” if you try access an array with an illegal index, that is with a negative number or with a number greater than or equal to its size.
Arrays are widely used with loops (for loops, while loops). There will be more sample program of arrays with loops tutorial.
Summary
An array is a group of similar typed variables that are referred to by a common name.
Array can be declared using indexes or literals.
Single dimensional array is widely used but we can have multi-dimensional.





No comments:
Post a Comment